The transformer (transformer) is a tool used to raise or lower the alternating voltage (AC)
The transformer consists of three basic components, namely:
- The first coil (primary) that as input.
- The second coil (secondary) are as output.
- The iron core that serves to amplify the magnetic field generated.
The working principle of a transformer that is, when the primary coil is connected to an alternating voltage source (AC), changes in electrical current in the primary coil lead to a changing magnetic field. Changing magnetic field is strengthened by the presence of an iron core and iron core is delivered to the secondary coil, so that the ends of the secondary coil induced emf will arise.
This effect is called mutual inductance (mutual inductance).
when the electric current flowing from the voltage source to the primary coil reversed (changed polarity) magnetic field generated will change direction so that the electric current generated in the secondary coil will change polarity.
The relationship between the primary voltage, the number of primary winding, secondary voltage, and the number of secondary windings, can be expressed by the equation:
Vp = primary voltage (volts)
Vs = secondary voltage (volts)
Np = number of primary windings
Ns = number of secondary windings
symbol Transformer
Based on the ratio between the primary winding and the number of secondary transformer windings there are two types:
- A step-up transformer is a transformer that converts alternating voltage is low to high, this transformer has a number of windings of the secondary coil are more than the number of the primary winding (Ns> Np).
- The step-down transformer is a transformer that converts alternating voltage is high to low, the transformer has primary coil windings amount more than the amount of the secondary winding (Np> Ns).
On transformer (transformer) the magnitude of the voltage issued by the secondary coil is:
1. In proportion to the number of secondary windings (Vs ~ Ns).
2. In proportion to the magnitude of the primary voltage (VS ~ VP).
3. Inversely proportional to the number of primary winding,
The use of transformers
The transformer (transformer) used in electrical equipment particularly those requiring changes or adjustments to the magnitude of an alternating voltage. Eg radio requires a voltage of 12 volts when 220 volts of electricity, it would require a transformer to convert an alternating electric voltage of 220 volts to an alternating electric voltage of 12 volts.
Examples of power tools that require a transformer is:
- TV
- Computers
- Photocopy machine
- Powerhouse
- Etc.
Examples of how to calculate the number of secondary windings:
To turn on the lamp voltage of 10 volts to 220 volts of electricity use the step-down transformer. If the number of windings of the transformer primary winding 1100, what is the number of turns on the secondary coil?
completion:
Note: Vp = 220 V
Vs = 10 V
Winding Np = 1100
Asked: Ns = ...........?

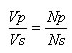



Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar